Currently, they are divided into three different categories:Cognitive enhancers are used by healthy individuals to shift consciousness into a wanted direction (for example, to be more alert, improve mood, or have better focus and motivation at work).
- Dietary supplements (such as citicoline or ashwagandha) -> this is what we concentrate on in this article and in the Biohacker´s Brain Nutrition Guide
- Synthetic compounds (such as piracetam)
- Prescription drugs (such as Ritalin)
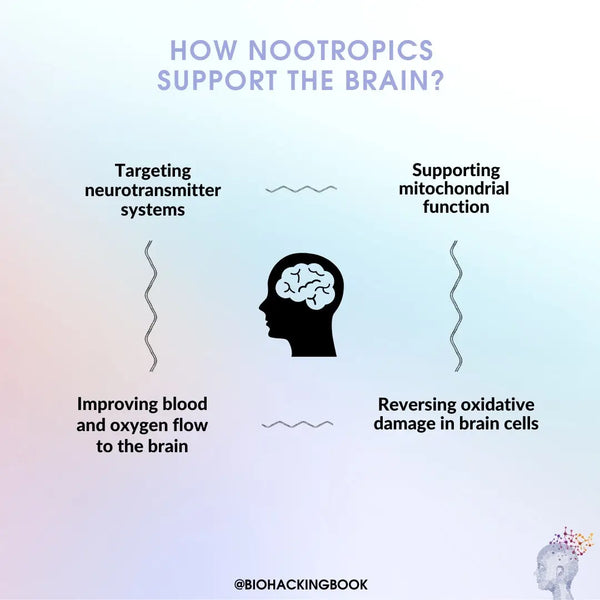
- Targeting neurotransmitter systems (such as dopaminergic, serotonergic or GABAergic systems).
- Increasing the function of brain cells’ mitochondria (energy factories of cells), which increases energy production in the brain.
- Dilating the blood vessels in the brain and consequently increasing blood and oxygen flow in the brain tissue.
- Reversing oxidative damage in brain cells, which can protect from memory diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Enhance learning and memory.
- Increase metabolism in the brain.
- Protect the brain against physical or chemical injury.
- Strengthen the regulative mechanisms of the brain.
- Are free from side effects or have minimal side effects and are non-toxic.
- Show benefits for the brain and enhanced brain function in clinical studies.
- Penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
- Have no major effects on blood pressure or heart rate.
N.B. Only a few natural substances fulfill all or most of these features, but when combined, one may achieve comprehensive effects on the brain. Read on...
Here is the list of Top 5 Natural Cognitive Enhancers and their unique effects on the brain
1. Choline and its metabolites (such as citicoline)
Choline is found in egg yolk, beef and fatty fish. It is widely needed in the body. Choline is crucial for brain development, detoxifying, muscle contraction, building the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and building cell membranes (synthesis of numerous phospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin). Choline is also important for DNA methylation in the brain, which means it helps to convert dangerous toxins into non-harmful compounds and alters the activity of proteins that encode learning and memory. Large-scale longitudinal studies have found that sufficient choline intake predicts better memory and cognitive functioning.
Choline is the building block of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) and influences its transmission in this cholinergic pathway. Acetylcholine is known for activating the sympathetic nervous system and improving alertness. In the brain, the cholinergic system connects brain areas called the hippocampus and amygdala, which help to form and recall spatial and emotional memories. The majority of the dietary choline is converted into citicoline, phosphatidylcholine and lecithin in the body. Extensive meta-analysis has also found citicoline to help memory and cognitive function recovery in people with cerebrovascular disease. CDP-choline also Improves attentional performance.
2. Rhodiola rosea (roseroot)
Roseroot (Rhodiola rosea) is one of the oldest herbaceous plants in the world. About 2,000 years ago, the famous Greek doctor Dioscorides (ca. 40–90) mentioned the roseroot (Lat. Rodia riza) in the early versions of one of the longest-lasting natural history books called De Materia Medica.
The active ingredients in Rhodiola include plant compounds that presumably affect neurotransmitters and opioid synthesis and have antioxidant properties. Out of the 140 isolated compounds, the most studied are rosavins (rosavin, rosarian and rosin) and salidroside, both found in the root of the plant.
Brain benefits of Rhodiola rosea:
- Can improve general well-being and motivation to work and reduce mental fatigue during stressful life periods.
- One study noticed that Rhodiola supplementation for two weeks reduced moderate stress and fatigue of workers after night duty.
- 1–4 week supplementation with Rhodiola rosea reduced everyday fatigue, burnout symptoms and stress, and cortisol levels.
- Animal models show that Rhodiola can improve serotonin levels, hippocampal growth and the longevity of hippocampal brain cells after depression.
- Rhodiola can improve attention and reduce errors made in tasks requiring attention and focus.
Image: Potential effects of roseroot in the body.
Source: Brown, R. & Gerbarg, P. & Ramazanov, Z. (2002). Rhodiola rosea: A Phytomedicinal Overview. HerbalGram 56: 40–52.
3. Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR)
The liver and kidneys naturally produce an amino acid called L-carnitine for energy production in the cells. Carnitine has a vital role in the cells where it participates in fatty acid transportation to the mitochondria. Carnitine is naturally found in animal products such as red meat, and it is also stored mainly in the muscles.
Acetyl-L-carnitine is known to have an important role in brain development, brain functioning, mood and cognition. ALCAR and other esters of carnitine can cross the blood-brain barrier and thus rapidly affect the brain cells.
Brain benefits of acetyl-L-carnitine:
- Protects the brain from damage, and acts as an antioxidant.
- Can improve mood and motivation in depressed and dysthymic populations.
- Can improve attention, concentration and energy levels in a population with chronic fatigue.
- Can increase mental energy and cognitive status (attention, memory, verbal fluency and mood) in the elderly.
4. Creatine monohydrate
Creatine is an organic molecule that is synthesized primarily in the liver and to a lesser extent in kidneys from amino acids glycine, arginine and methionine. Creatine functions as phosphate storage for energy production in the mitochondria. Red meat and fish are the richest dietary sources of creatine. A pound of uncooked beef and salmon provides about 1–2 grams of creatine.
Creatine has been used as a dietary supplement for many decades (creatine monohydrate) because of its capability to significantly increase force generation in the skeletal muscles. What has been a lesser-known field of research on supplementing with creatine is its ability to have a significant effect on overall cognitive performance. The brain has several mechanisms to take up creatine and also to regulate the intake and levels in the brain.
Brain benefits of creatine supplementation:
- In young adults, a short-term (6 weeks) supplementation on creatine monohydrate significantly improved general brain performance including working memory and processing speed.
- Based on a 2018 systematic review of randomized and controlled trials, creatine monohydrate may improve short-term memory and intelligence of stressed individuals and/or healthy individuals with the biggest potential in the aging population.
- In young adult female vegetarians, when compared to those who consume meat, creatine supplementation resulted in better memory. This preliminary evidence suggests that vegetarians respond more readily (i.e., are more sensitive) to creatine supplementation.

5. Caffeine + L-theanine
Caffeine is the most widely used psychoactive substance in the world and also one of the most popular nootropics. Caffeine can be isolated from 60 different plants, but the most common sources of caffeine include coffee beans, cacao, black and green tea, yerba mate, guarana, guayusa and kola nuts.
Caffeine increases alertness because it blocks adenosine receptors in the brain. When caffeine blocks adenosine receptors, it consequently prevents the feeling of sleepiness but also promotes neurotransmission of dopamine and acetylcholine, which further increases wakefulness, motivation, alertness and cognitive function.
L-theanine is an amino acid found in tea leaves and some mushrooms. It was discovered by Japanese scientists in 1949 and has recently been under scientific research due to its calming effects. L-theanine also produces a noticeable relaxing effect in humans by increasing the so-called alpha waves in the brain.
Brain benefits of caffeine include:
- In low doses (~20–50 mg) it enhances long-term memory, attention, and reaction times and reduces anxiety.
- It can improve reaction times and sustained attention, especially when combined with L-theanine.
- Depending on your genes/goals and general arousal, take anything between 10–200 mg of caffeine at once.
- Slow metabolizers have better effects at lower doses.
Brain benefits of L-Theanine include:
- Increases calmness and reduces tension.
- Increases alpha waves in the brain (gradually from ingestion up to at least two hours).
- Can improve sustained attention on a task, especially when combined with caffeine.
- L-theanine has also been shown to reduce symptoms of non-clinical insomnia in people with anxiety and ADHD.
///





